While upgrading _NetScaler version from 13.0 to 13.1 we need to convert the classic polices to advance polices as it is not supported by NetScaler v 13.1
Before that take full backup of the both primary and secondary NetScalers and also take the backup if you have a customized theme. Especially during this upgrade take backup of httpd.conf and ns.conf and save it in the local machine.
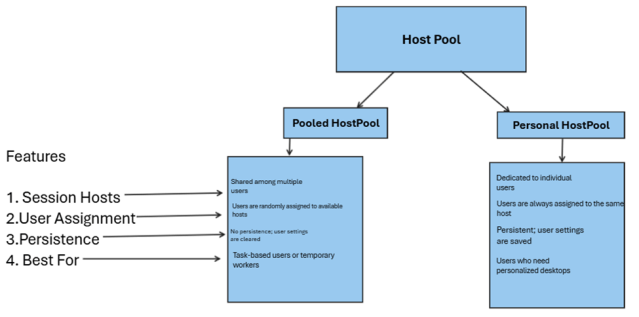
Difference between Classic polices and Advance polices.
1. Any expression starts with REQ comes under classic polices
2. Any policies contain == comes under classic policies
3. Advance polices start with HTTP
4. Advance polices contain EQ and Brackets
Use the NSPEPI tool to convert from classic to advance policy.
1. Login to primary node through Putty and run the following command to convert policy.
nspepi -f /nsconfig/ns.conf
2. Once converted the policy (ns.conf config file), we can see the converted file as a new file with a prefix, ‘new’.
3. The warnings and error file has the same name as input file but with a prefix ‘warn_’ added to the file name.
Verify the warning before upgrading the ADC. If warn.conf file only contains the warning for
compression polices then we can ignore as compression polices not required to convert to
advance. Other policies should be converted successfully before proceeding. Contact Citrix support if you get warning or error in converting other policies.
Once polices are converted, copy the new_ns.conf then rename the existing ns.conf as
ns_old.conf. Rename new_ns.conf as ns.conf.
Then reboot the NetScaler for polices to take effect.
4. Take back up of the customized portal theme from the path: /var/netscaler/logon directory.
Steps to upgrade the NetScaler
1. To upload the software to the Citrix ADC with WinSCP.
2. Create a directory for new build version under /var/nsinstall (e.g. /var/nsinstall/Build)
3. Copy the software from your computer to the /var/nsinstall/B uild directory in the NetScaler.
4. Use Putty to open an SSH connection to the appliance.
5. At the command prompt, type shell.
6. Type cd /var/nsinstall/build-13. 1-xx. xx_nc_64 to change to the nsinstall directory
7. To unpack the software, type tar – zxvf build-13.1-xx.xx_nc_64.tgz
8. To start the installation, type ./installns
9. NetScaler will reboot once the installation is completed, To verify the version type, Show ns version
Try to access the GUl Console of your NetScaler ADC, if GUl is not working then follow the below steps. Check the Citrix article CTX277615 for more details.
1. Backup the existing httpd.conf from /nsconfig directory of Primary.
2. Delete the /nsconfig/httpd.conf file from Primary.
3. Delete the the /nsconfig/httpd.conf from Secondary.
4. Reboot the Secondary appliance.
5. After reboot, failover to the secondary appliance and then reboot the old primary.
Or follow the below steps
Take the backup of httpd.conf file from “/nsconfig/httpd.conf” location and delete the “httpd” file from nsconfig location and etc location.
Now edit the httpd file location and replace the libphp7.so to libphp.so in httpd.conf file and save it.
Now place the httpd.conf file in etc and nsconfig location to fix the issue. Reload the GUI page to access the NetScaler console.